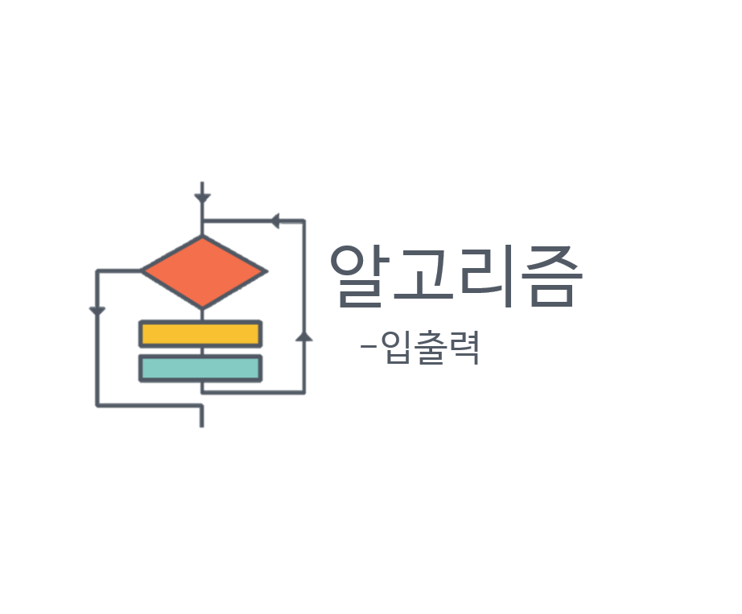


10950
입력받은 두 정수의 값을 합하여 출력

1차
import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int a; a = sc.nextInt(); for(int i=0;i<a;i++) { int b = sc.nextInt(); int c = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println(b+c); } } }
답안
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.StringTokenizer; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); StringTokenizer st; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " "); sb.append(Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()) + Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken())); sb.append('\n'); } System.out.println(sb); } }
10951

1차 (scanner)
import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); while(sc.hasNextInt()) { int a = sc.nextInt(); int b = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println(a+b); } sc.close(); } }
2차 (buffer)
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.StringTokenizer; public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); StringTokenizer st; String str; while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) { st = new StringTokenizer(str, " "); int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); sb.append(a + b).append("\n"); System.out.print(sb); sb.setLength(0); } } }
10952

1차 (Scanner)
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.StringTokenizer; public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); StringTokenizer st; String str = null; int a=1; int b=1; while (a!=0&&b!=0) { str = br.readLine(); st = new StringTokenizer(str, " "); a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); if(a!=0&&b!=0) { sb.append(a + b).append("\n"); } } System.out.println(sb); } }
핵심변경
if(a==0&&b==0) { break; }
11022
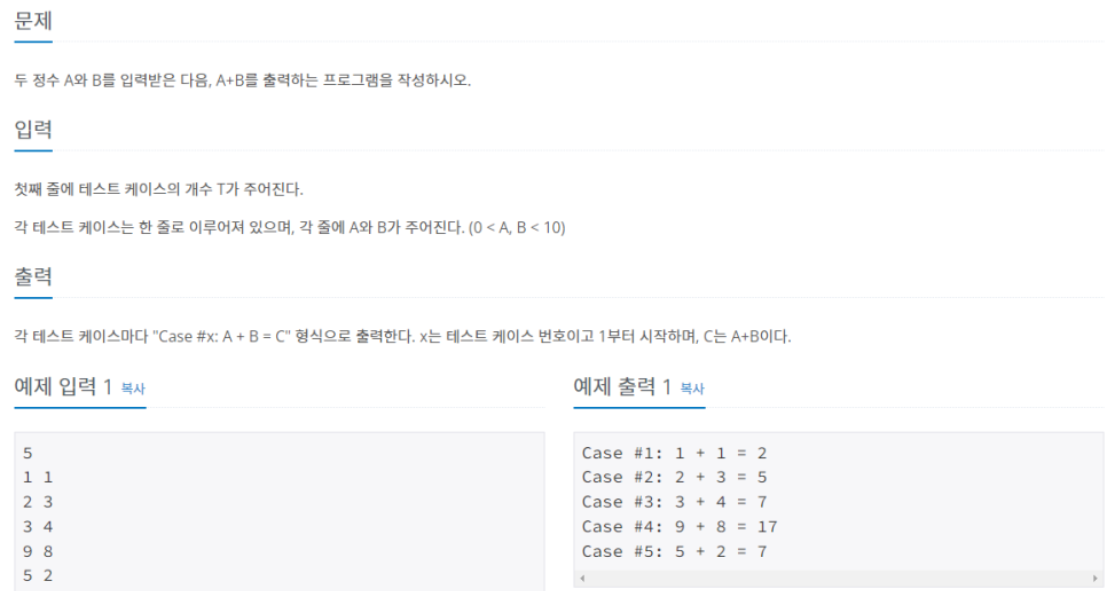
입력받은 값을 변수에 담는 방식으로 변경
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.StringTokenizer; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); StringTokenizer st; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " "); //중요 int A=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); //중요 int B=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); sb.append("Case #"+(i+1)+": "+A+" + "+B+" = "+(A+B)); sb.append('\n'); } System.out.println(sb); } }
11718
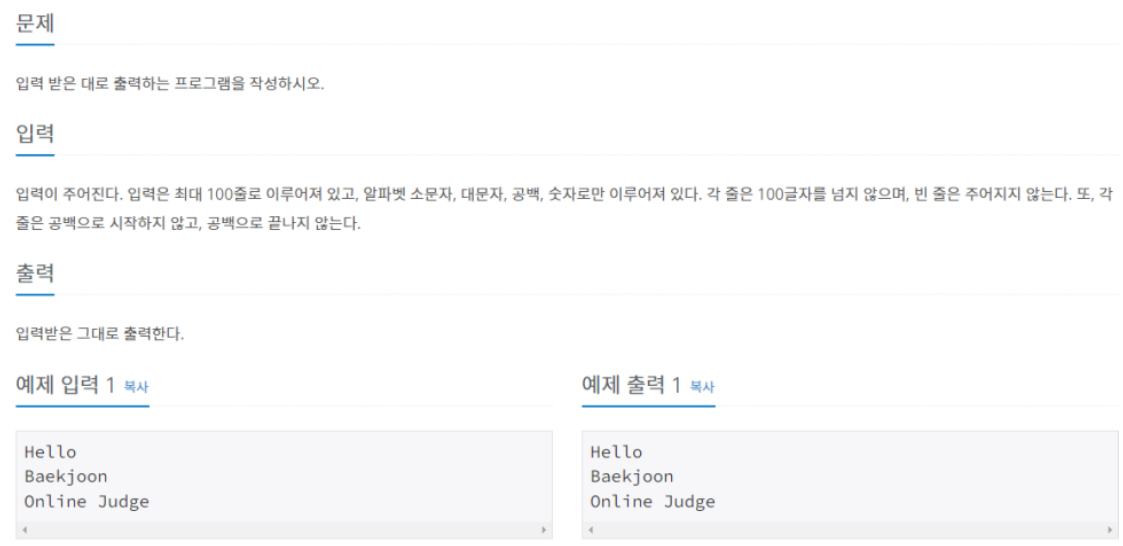
받은값이 존재할때까지 반복
1차 sc
import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); while(sc.hasNextLine()) { System.out.println(sc.nextLine()); } sc.close(); } }
2차 readline
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.StringTokenizer; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); String str; while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(str); } } }
해당 코딩으로 확인 할 수 있는점은
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
해당 코딩은 공백을 기점으로 값을 붙이기 위함이였다는 것.
값을 받는것은 br.readLine() 으로만으로도 충분하다는 것.
11720

1. String 값을 원소로 바꿔서 더해준다.
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int N = in.nextInt(); String a = in.next(); in.close(); int sum = 0; for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) { sum += a.charAt(i)-'0'; } System.out.print(sum); } }
2. byte로 받는다
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.IOException; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); br.readLine(); // N 은 쓸모가 없으므로 입력만 받는다. int sum = 0; for(byte value : br.readLine().getBytes()) { sum += (value - '0'); // 또는 (a-48) } System.out.print(sum); } }
두 코딩 모두 값을 UTF-16 인코딩 방식을 따르는데, [UTF-16 (유니코드) 의 앞부분은 아스키코드와 호환되기 때문에] '0' 이라는 문자는 46의 숫자와 같다.
UTF-16 인코딩에 맞게 각 문자의 값을 저장하므로 반드시 '0' 또는 48 을 빼주어야 한다.
11721
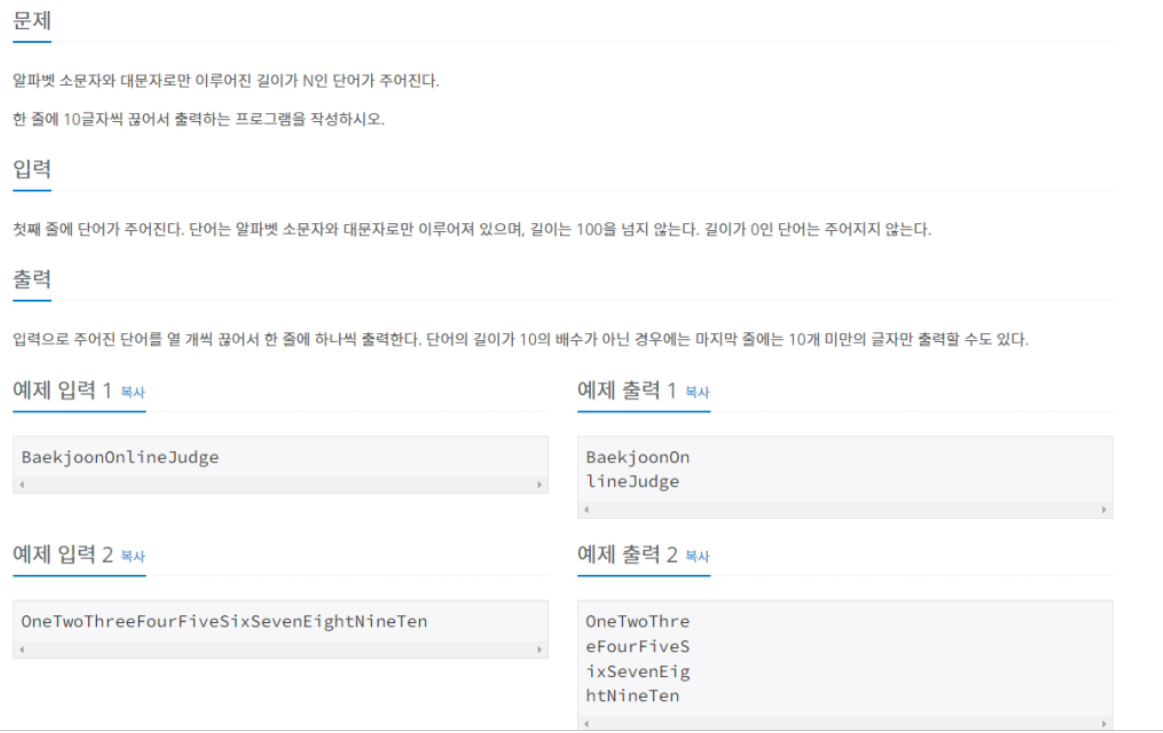
1차 substring으로 자르기
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.StringTokenizer; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String str = br.readLine(); int count = str.length(); int head = count / 10; int tail = count % 10; int sub = 0; for (int i = 0; i < head; i++) { String output = str.substring(sub, sub + 10); sub += 10; System.out.println(output); } String output = str.substring(sub, sub + tail); System.out.println(output); } }
2741
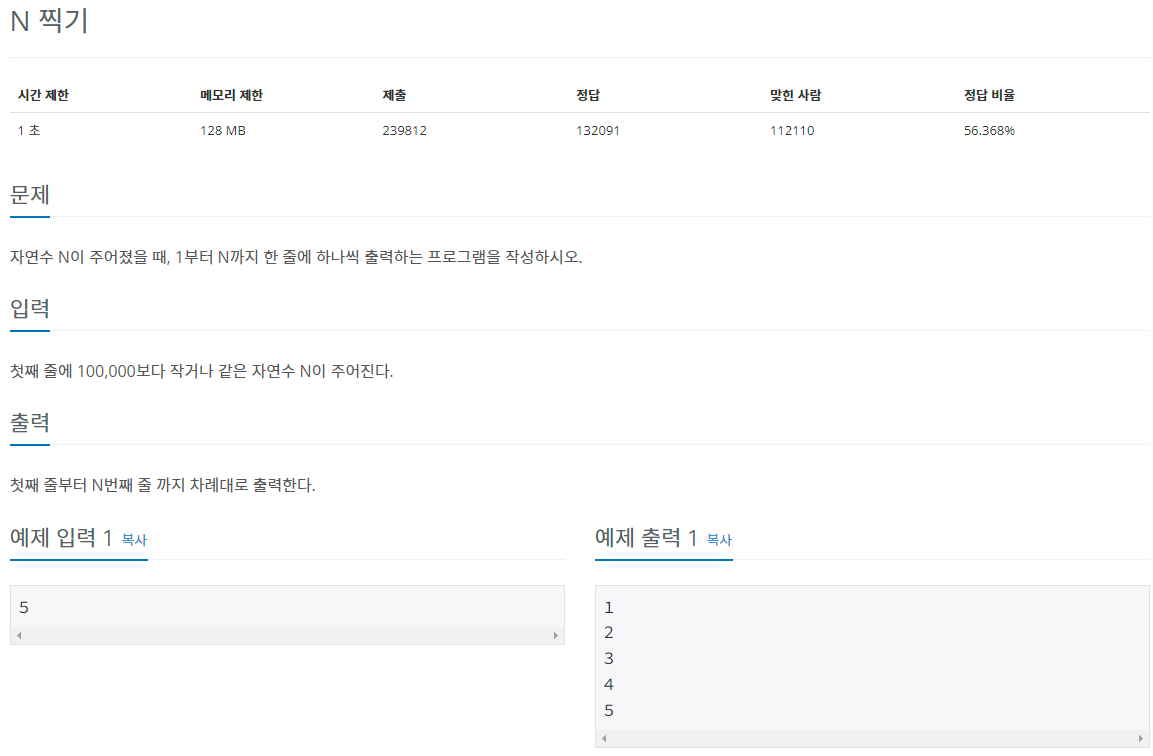
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int N = sc.nextInt(); int A=1; while(A<=N) { System.out.println(A); A++; } } }
1부터 출력해야 해서 입력 받은 수 까지 A를 증가시킴.
2742
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int N = sc.nextInt(); while(N>0) { System.out.println(N); N=N-1; } } }
2739

import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int N = sc.nextInt(); for(int i=1; i<10; i++) { System.out.println(N +" * "+i+" = "+N*i); } } }
이중 배열 입력받고 출력하기
input 값
1 3 3 6 7
8 13 9 12 8
4 16 11 12 16
2 4 1 23 2
9 13 4 7 3
package test; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.StringTokenizer; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { int [][]array = new int[5][5]; int pari; BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st; for(int i=0; i<5; i++) { st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," "); for(int j=0; j<5; j++) { pari = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); array[i][j]=pari; } } for(int i=0; i<5; i++) { for(int j=0; j<5; j++) { System.out.print(array[i][j]+" "); } System.out.println(); } } }
한줄 입력받고 초기화 시키고 다시 입력받는식으로 함.
.end
'알고리즘(BOJ) > Bronze' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 - 캠핑 4796 (0) | 2023.03.13 |
|---|